Rice Cooker related
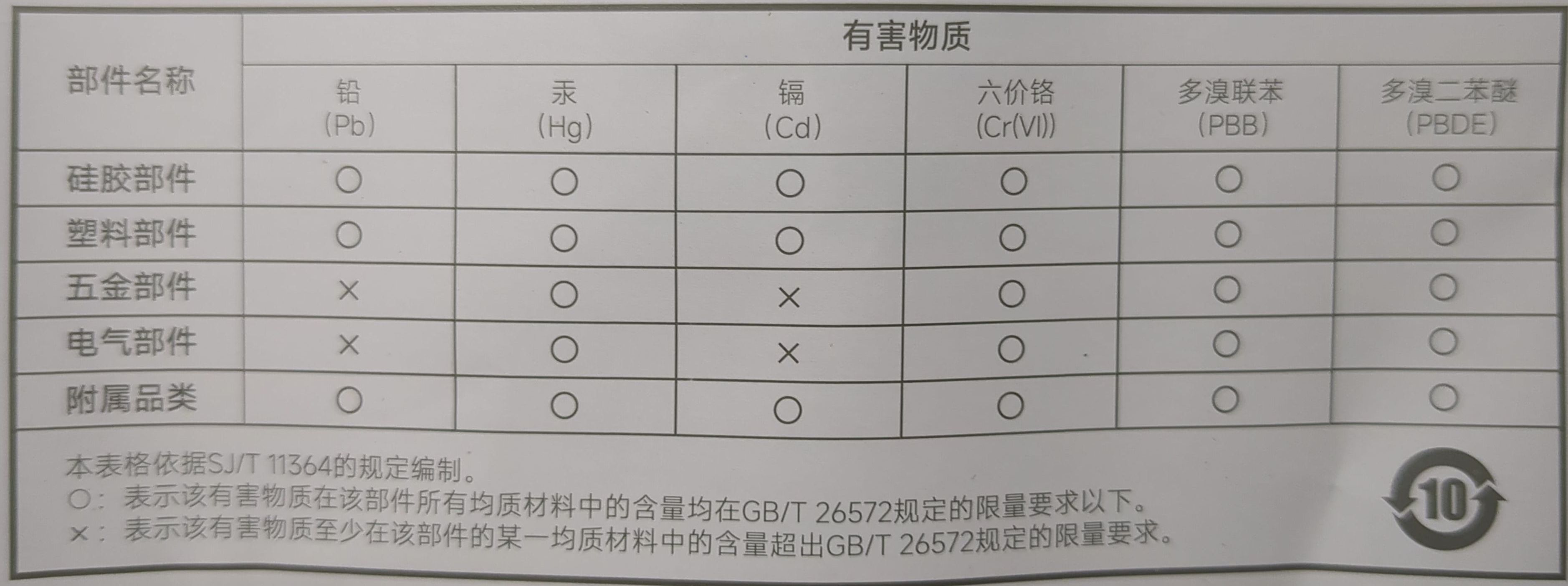
GB/T 26572 is a Chinese national standard that specifies the limits for certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic products, while EU/International standards, such as the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) Directive, set similar limits for the European Union and other countries. Here's a comparison of the limits for Pb, Hg, Cd, Cr(VI), PBB, and PBDE in GB/T 26572 and EU/International standards:
- Lead (Pb):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight ( Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
- Mercury (Hg):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight (Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
- Cadmium (Cd):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.01% (100 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: ≤ 0.01% (100 ppm) by weight (Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight (Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: prohibited (Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE):
- GB/T 26572: ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight
- EU RoHS: prohibited (Directive 2011/65/EU, Annex II)
Key differences:
- PBB and PBDE are prohibited in the EU RoHS, while GB/T 26572 allows a limit of ≤ 0.1% (1000 ppm) by weight.
- The limits for Pb, Hg, Cd, and Cr(VI) are the same in both GB/T 26572 and EU RoHS.
Note that these limits may be subject to change, and it's essential to check the latest versions of the standards and directives for the most up-to-date information. Additionally, other international standards, such as IEC 63000, may have similar or more stringent requirements.